What is music production ? A fascinating and rewarding journey that allows you to bring your musical ideas to life. Whether you’re a budding musician or simply have a passion for creating music and still at your beginnings, learning the art of music production can open up a whole new world of creative possibilities.
At its core, music production involves the process of creating and manipulating sound to produce a final musical composition. It involves a combination of technical skills, musical knowledge, and artistic creativity. From choosing the right equipment to mastering advanced techniques, the music production definition offers endless opportunities for self-expression and exploration.
Why Learn Music Production?
There are numerous reasons why learning how to make your own music can be beneficial for beginners. First and foremost, making your own music allows you to have complete control over your music. Instead of relying on others to bring your ideas to life, you can take charge and create the sound that you envision. This level of creative freedom is empowering and can lead to a deeper connection with your music.
Moreover, learning how to become a music producer opens up doors to various career opportunities. Whether you aspire to be a producer, sound engineer, or a professional musician, having a solid understanding of how to be a music producer can significantly enhance your chances of success in the industry. It equips you with the necessary skills to produce high-quality recordings, collaborate with other artists, and navigate the ever-evolving landscape of the music business.
Music Production Equipment for Beginners
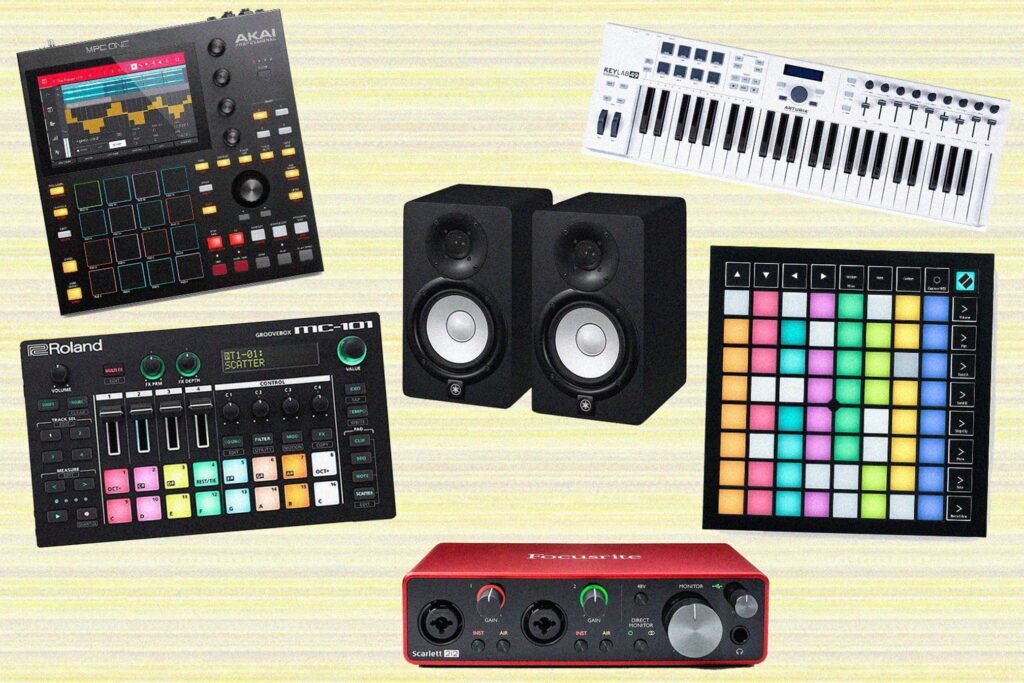

Getting started in music production doesn’t have to break the bank. There is a wide range of affordable equipment available that is perfect for beginners. Here are some essential pieces of equipment you’ll need to kickstart your journey on how to start making music, or how to start producing music:
- Computer: A reliable computer is the heart of any music production setup. Look for a machine with ample processing power and storage capacity to handle the demands of recording and editing audio.
- Audio Interface: An audio interface acts as the bridge between your computer and other audio devices. It allows you to connect microphones, instruments, and studio monitors to your computer for recording and playback.
- Studio Monitors: Studio monitors are specialized speakers designed for accurate and transparent sound reproduction. They are essential for mixing and mastering your music, as they provide a true representation of how your music sounds.
- MIDI Keyboard: A MIDI keyboard is a versatile tool that allows you to play virtual instruments and control various aspects of your music production software. It’s a great addition for composing melodies, programming drum beats, and experimenting with different sounds.
- Microphone: A good quality microphone is crucial for capturing clear and professional-sounding vocals and acoustic instruments. Look for a microphone that suits your recording needs, whether it’s for vocals, instruments, or podcasts.
These are just a few examples of the essential equipment you’ll need to get started in music production. As you progress and refine your skills, you may choose to invest in additional gear to enhance your setup.
Essential Software
Alongside the hardware, having the right music software is equally important for music production. Here are some essential software programs that beginners should consider:
- Digital Audio Workstation (DAW): A DAW is the central software that allows you to record, edit, and mix your music. Popular DAWs include Ableton Live, Logic Pro, and FL Studio. Each DAW has its own unique features and workflow, so it’s important to choose one that suits your needs and preferences.
- Virtual Instruments and Sample Libraries: Virtual instruments and sample libraries are software-based instruments that allow you to create realistic sounds without needing physical instruments. These can range from virtual pianos and synthesizers to orchestral instruments and drum kits. Many DAWs come with a selection of built-in virtual instruments, but you can also find a wide variety of third-party options.
- Effects Plugins: Effects plugins are software programs that modify and enhance the sound of your recordings. They can be used for tasks such as equalizing, compressing, reverb, and delay. There are numerous free and paid plugins available, offering a vast array of creative possibilities.
- Audio Editing Software: In addition to your DAW, having dedicated audio editing software can be useful for tasks such as cleaning up recordings, removing background noise, and editing individual audio files. Adobe Audition and Audacity are popular choices for audio editing.
Remember, the software you choose is a personal preference, and it’s important to experiment and find the tools that work best for you. Many software companies offer free trials, so take advantage of those to test out different options before committing to a purchase.
Basic Music Production Techniques for Beginners

Now that you have your equipment and software in place, it’s time to dive into some basic music production techniques. These techniques form the foundation of music production and will help you get started on the right foot. Here are a few essential music production techniques to get you started:
- Recording: Whether you’re recording vocals, instruments, or both, it’s important to set up your recording environment correctly. Find a quiet space, position your microphone properly, and experiment with microphone techniques to achieve the desired sound.
- MIDI Programming: MIDI programming allows you to create melodies, chord progressions, and drum patterns using virtual instruments. Familiarize yourself with piano roll editors and step sequencers within your DAW to create compelling musical arrangements.
- Arrangement: The arrangement of your music is crucial in creating a captivating listening experience. Experiment with different song structures, build-ups, and breakdowns to keep your listeners engaged from start to finish.
- Mixing: Mixing is the process of balancing and enhancing the individual elements of your music. Learn the basics of EQ, compression, and reverb to create a well-rounded mix. Don’t be afraid to experiment and trust your ears.
- Mastering: Mastering is the final step in the music production process. It involves fine-tuning the overall sound of your music and preparing it for distribution. Focus on achieving a balanced frequency response, optimal loudness, and consistency across different playback systems.
These basic techniques will provide a solid foundation for your music production journey. As you gain more experience and confidence, you can explore more advanced techniques and experiment with different genres and styles.
Music Production Courses for Beginners

While self-learning is a viable option for many, enrolling in a music production course can greatly expedite your progress and provide valuable guidance along the way. Here are some reasons why learning about music production and producing music for beginners through courses are beneficial:
- Structured Learning: Music production courses are designed to provide a structured learning experience, ensuring that you cover all the essential topics and techniques in a logical progression. This can save you time and help you avoid getting overwhelmed by the vast amount of information available.
- Expert Guidance: Courses are typically led by experienced instructors who can provide valuable insights, tips, and feedback. Their expertise can help you overcome challenges and refine your skills more efficiently.
- Collaborative Environment: Courses often provide opportunities to collaborate with fellow students, fostering a supportive and creative environment. Collaborating with others can expose you to different perspectives and ideas, helping you grow as a music producer.
- Networking Opportunities: Music production courses can connect you with like-minded individuals and industry professionals, opening doors to potential collaborations, gigs, and future opportunities.
When choosing music production courses, consider factors such as the course curriculum, instructor qualifications, student reviews, and the level of support provided. Look for courses that align with your specific goals and interests, whether it’s electronic music production, sound engineering, or film scoring.
Here is a review to Timbaland’s MasterClass course/training!
Choosing the right music production course for beginners
With countless online courses in music production available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a music production course for beginners:
- Course Curriculum: Review the course syllabus to ensure that it covers the topics and techniques you’re interested in learning. Look for courses that strike a balance between theory and practical application.
- Instructor Qualifications: Research the instructors’ backgrounds and qualifications. Check if they have relevant industry experience and a track record of success. It’s also helpful to find instructors who specialize in the genre or style of music you’re interested in.
- Student Reviews and Testimonials: Read reviews and testimonials from past students to get an idea of their experiences with the course. Look for courses that have positive feedback and success stories from previous attendees.
- Support and Resources: Consider the level of support and resources provided by the course. This can include access to forums, Q&A sessions, tutorial videos, and downloadable course materials. A course that offers ongoing support can greatly enhance your learning experience.
- Budget and Time Commitment: Determine your budget and the time you’re willing to commit to the course. Some courses require a significant investment, while others are more affordable or even free. Consider your financial situation and availability before making a decision.
Remember, the right music production course is subjective and depends on your individual goals, learning style, and preferences. Take the time to research and compare different options to find the course that best suits your needs.
Tips for Getting Started in Music Production
Embarking on your music production journey can be both exciting and daunting. To help you get started on the right track, consider these essential music production tips:
- Set Realistic Goals: Start by setting realistic and achievable goals. Whether it’s finishing a song, learning a new technique, or mastering a specific piece of equipment, having clear goals will keep you motivated and focused.
- Practice Consistently: Consistency is key in mastering any skill. Dedicate regular practice time to music production, even if it’s just a few hours a week. Over time, consistent practice will yield significant progress.
- Experiment and Be Curious: Don’t be afraid to experiment and think outside the box. Music production is a creative endeavor, and innovation often comes from pushing boundaries and trying new things. Embrace curiosity and allow yourself to make mistakes along the way.
- Learn from the Masters: Study the work of established music producers and engineers. Analyze their techniques, dissect their arrangements, and try to understand their creative choices. Learning from the masters can provide valuable insights and inspiration for your own productions.
- Join Online Communities: Engage with online communities and forums dedicated to music production. Connect with fellow producers, share your work, and seek feedback. Online communities offer a wealth of knowledge and can be a source of inspiration and encouragement.
Remember, progress in music production is a journey, and it’s important to enjoy the process. Celebrate small victories, be patient with yourself, and never stop learning.
Advanced Production Techniques for Beginners
Once you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to delve into advanced music production techniques. Here are a few strategies that can elevate your productions to the next level:
- Sound Design: Sound design involves creating unique and interesting sounds using synthesizers, samplers, and effects. Experiment with different synthesis techniques, sample manipulation, and sound sculpting to add depth and character to your music.
- Automation: Automation allows you to control various parameters in your music production software over time. Use automation to create dynamic changes in volume, panning, effects, and more. This adds movement and interest to your compositions.
- Parallel Processing: Parallel processing involves blending multiple versions of a sound together to create a more complex and polished sound. Experiment with parallel compression, EQ, and saturation to add warmth, depth, and clarity to your mix.
- Creative Sampling: Sampling is a technique that involves taking small snippets of audio and manipulating them to create new sounds. Explore creative sampling techniques such as time-stretching, pitch-shifting, and granular synthesis to create unique textures and atmospheres.
- Mixing in Surround Sound: If you have access to a surround sound setup, consider experimenting with mixing in a multi-channel environment. This allows for a more immersive listening experience and can add an extra dimension to your music.
These advanced techniques require a deeper understanding of music production principles and a willingness to experiment. Don’t be afraid to push the boundaries and explore new sonic territories.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
As with any creative endeavor, music production can come with its fair share of challenges and roadblocks. Here are some common issues that beginners may encounter and music production troubleshooting tips on how to address them:
- Latency: Latency refers to the delay between when you play a note or start recording and when you hear the sound. To minimize latency, ensure that your audio interface drivers are up to date, adjust buffer settings in your DAW, and use low-latency monitoring options if available.
- Clipping and Distortion: Clipping occurs when the audio signal exceeds the maximum level that can be accurately recorded or played back. To avoid clipping, monitor your levels and use gain staging techniques to ensure a healthy signal-to-noise ratio.
- Muddy Mixes: A muddy mix lacks clarity and definition, with sounds overlapping and competing for space. To address this issue, use EQ to carve out space for each element, apply selective compression, and consider panning and spatial effects to create separation.
- Lack of Inspiration: Creative blocks are common in music production. To overcome them, take breaks, listen to different genres, experiment with new sounds, and collaborate with other musicians. Sometimes, stepping away from your project for a while can bring fresh inspiration.
- Technical Glitches: Technical glitches can disrupt your workflow and lead to frustration. Regularly update your software and plugins, save your work frequently, and maintain backups of your projects to minimize the impact of technical issues.
Remember, troubleshooting is an essential part of the learning process, and it’s important to approach challenges with a problem-solving mindset.
Conclusion
Congratulations on embarking on the ultimate music production journey for beginners! By learning music production, you’ve opened the door to endless creative possibilities and potential career opportunities. Remember to start with the basics, invest in the right equipment and software, and consider enrolling in a music production course to expedite your progress. Practice consistently, experiment with different techniques, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes. With dedication and perseverance, you’ll transform from a novice into a maestro of music production. Enjoy the journey!
This post may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you.








