Audio compression plays a crucial role in the world of music production. It is a technique used to control the dynamic range of audio signals, allowing for a more balanced and polished sound. Whether you’re a seasoned producer or just starting out, understanding the basics of audio compression is essential for achieving professional-quality recordings.
Understanding the Basics of Audio Compression
So, what exactly is compression in music? Compression is the process of reducing the dynamic range of an audio signal. Dynamic range refers to the difference between the loudest and softest parts of a sound. By compressing the dynamic range, you can bring up the quieter elements and control the peaks, resulting in a more consistent and even sound.
What does compression do? Well, it acts as an automatic volume control, adjusting the level of the audio signal based on its input. When the signal exceeds a certain threshold, the compressor kicks in and reduces the gain, resulting in a more controlled and uniform sound. This can be especially useful for vocals, drums, and other instruments with varying levels.
The Purpose of Audio Compression in Music Production
The primary purpose of audio compression in music production is to enhance the overall sound quality and improve the mix. By reducing the dynamic range, compression allows for a more balanced and controlled sound, ensuring that no elements get lost in the mix or overpower the others. It helps to bring out the details in a recording and make it more pleasing to the listener’s ear.
Another important purpose of audio compression is to ensure that the audio signal doesn’t overload or clip. Certain instruments or vocal performances can have sudden peaks that exceed the maximum level, leading to distortion. Compression helps to tame these peaks and prevent any unwanted distortion, ensuring a clean and professional-sounding mix.
How Does Audio Compression Work?
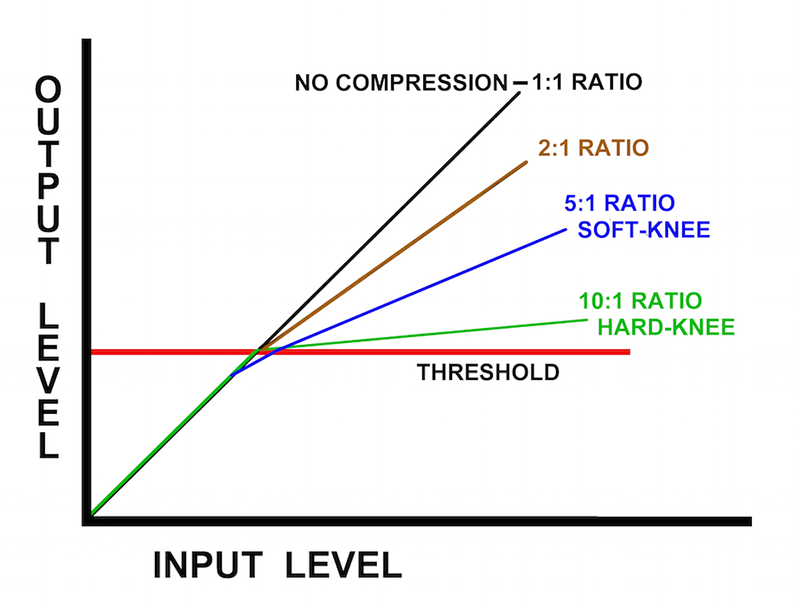
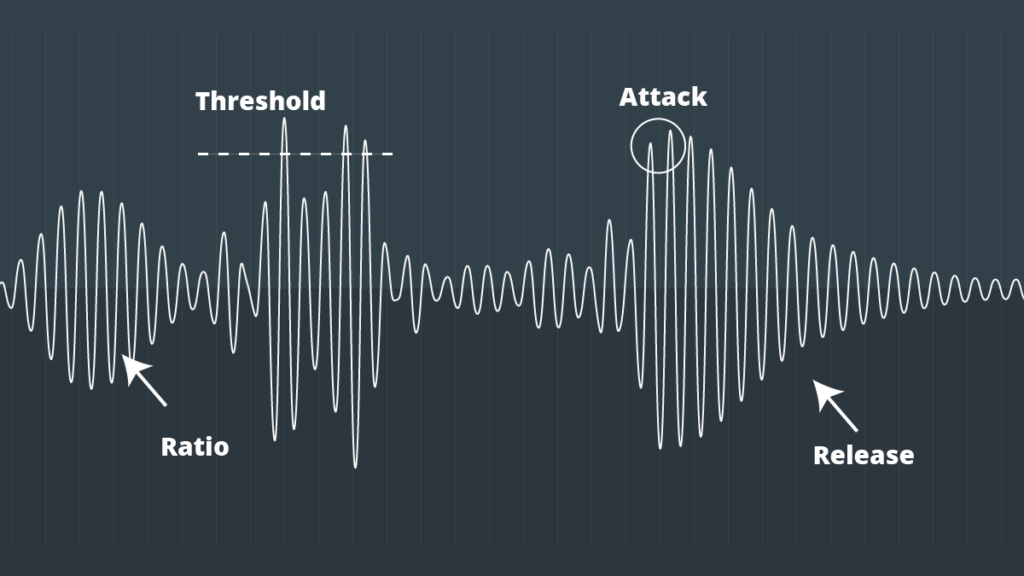
To understand how audio compression works, let’s take a closer look at the key parameters and settings involved. The most important parameter in compression is the threshold. This determines the level at which the compressor starts to reduce the gain. When the audio signal exceeds the threshold, the compressor kicks in and begins to apply gain reduction.
The next important parameter is the ratio, which determines the amount of gain reduction applied to the signal. For example, a ratio of 4:1 means that for every 4dB the signal exceeds the threshold, the output level will only increase by 1dB. A higher ratio results in more compression, while a lower ratio provides a more subtle effect.
Another essential setting is the attack time, which determines how quickly the compressor responds to the audio signal exceeding the threshold. A faster attack time will catch the peaks more quickly, while a slower attack time allows for more transient detail to come through before compression is applied. The release time determines how long it takes for the compressor to stop reducing the gain once the signal falls below the threshold.
Different Types of Audio Compressors

There are several types of audio compressors, each with its own unique characteristics and sonic qualities. Let’s explore some of the most common types:
- VCA Compressors: VCA (Voltage-Controlled Amplifier) compressors are known for their transparent and clean sound. They are often used for subtle compression and are suitable for a wide range of musical genres.
- Optical Compressors: Optical compressors, also known as LA-2A-style compressors, have a smooth and warm sound. They are particularly popular for vocals and acoustic instruments, adding a pleasing coloration to the sound.
- FET Compressors: FET (Field-Effect Transistor) compressors are known for their fast attack times and aggressive sound. They are commonly used for drums and electric guitars, providing a punchy and energetic character to the sound.
- Tube Compressors: Tube compressors, as the name suggests, use vacuum tubes to achieve compression. They impart a warm and vintage character to the sound, making them popular for adding a classic analog vibe to recordings.
Benefits of Using Audio Compression in Music Production
Now that we have a better understanding of the basics of audio compression, let’s explore the benefits it brings to music production:
- Controlled Dynamics: One of the main benefits of using audio compression is the ability to control the dynamic range of a mix. By compressing the peaks and bringing up the quieter elements, you can achieve a more balanced and controlled sound.
- Enhanced Clarity: Compression can help bring out the details in a recording, making it more defined and clear. It can emphasize the subtle nuances of a performance and ensure that no elements get lost in the mix.
- Improved Mix Consistency: When working with multiple tracks in a mix, compression can help ensure that all elements sit well together. It can even out the levels and provide a more cohesive and professional-sounding result.
- Prevention of Distortion: Compression can prevent audio signals from overloading or clipping, which can lead to unwanted distortion. By taming the peaks, compression ensures a clean and distortion-free sound.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Audio Compression
While audio compression is a powerful tool, it’s important to use it properly to avoid common pitfalls. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
- Over-compression: Applying too much compression can result in a lifeless and unnatural sound. It’s important to find the right balance and use compression only where it’s needed.
- Improper Attack and Release Settings: Choosing the wrong attack and release times can lead to a lack of transparency or an overly squashed sound. Experimenting with different settings and listening carefully is key to achieving the desired result.
- Ignoring the Mix Context: It’s crucial to consider the overall mix when applying compression. What might sound good on an individual track might not work well in the context of the entire mix. Always listen to how the compressed track interacts with the other elements.
Tips for Achieving the Desired Compression Ratio
Finding the right compression ratio can be a bit of a balancing act. Here are some tips to help you achieve the desired compression ratio:
- Start with a Low Ratio: Begin with a low compression ratio and gradually increase it until you achieve the desired effect. It’s better to err on the side of subtlety and make small adjustments as needed.
- Use Your Ears: Don’t solely rely on visual meters or presets. Listen carefully to the effect of compression on the sound and make adjustments based on what your ears tell you.
- Experiment with Different Attack and Release Times: The attack and release times play a significant role in shaping the sound. Experiment with different settings to find the right balance between control and transparency.
Using Audio Compression Creatively in Music Production
While compression is commonly used for controlling dynamics, it can also be used creatively to shape the sound in unique ways. Here are a few creative techniques:
- Parallel Compression: Also known as New York compression, this technique involves blending a heavily compressed signal with the uncompressed original. It can add sustain, punch, and thickness to the sound.
- Sidechain Compression: Sidechain compression is often used in electronic dance music to create the “pumping” effect. By triggering the compressor with a separate audio source, you can make certain elements stand out in the mix.
- Emphasizing Transients: By using a fast attack time and a high ratio, you can emphasize the transients of a sound, making it more punchy and upfront.
Conclusion
Audio compression is an essential tool in music production, allowing for more controlled and balanced recordings. By understanding the basics of audio compression, the purpose it serves, and how it works, you can take your music production skills to the next level. Remember to avoid common mistakes, experiment with different settings, and use compression creatively to achieve the desired sound. With practice and careful listening, you’ll be able to harness the power of audio compression and create professional-quality music.
Start experimenting with audio compression in your own music productions today and discover the transformative effects it can have on your sound.
This post may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you.








