In the fast-paced world of music production, mastering the art of file management with a music hard drive is not merely an option, but a necessity. Proper organization of music files, whether it’s sorting them into folders by project, date, or other relevant categories, streamlines your workflow and boosts efficiency. Moreover, adopting concise and descriptive file naming and ensuring regular backups can protect your project from potential data loss, while choosing a digital audio workstation (DAW) that complements these practices can greatly enhance your production setup. For music producers, ensuring your hard drive for music is optimized with standardized file formats and bit depths across systems also simplifies collaboration and project management.
Essentials of File Organization
To master file organization on your music hard drive, consider the following essentials that every music producer should implement for effective production:
- Subfolder Creation Based on Music Genres:
- Classical, Pop, Soundtracks, etc.
- Further categorization by sub-genres for detailed organization
- Example: Classic Rock > Rolling Stones Albums > Individual Albums + Miscellaneous Singles
- Metadata and ID3 Tags:
- Correct ID3 tags storing song title, artist, and album
- Fill in metadata for each song to simplify searching and sorting
- Update metadata when adding new music to ensure consistency
- Music Management Software:
- Utilize software like MediaMonkey and MusicMatch Jukebox for managing files
- Leverage music managers that allow for SMART playlists creation
- File Naming and Playlists:
- Use a clear and consistent naming system: Artist Name – Album Title – Track Number
- Create playlists based on themes or moods
- Alphabetize music by artist to keep albums together and simplify finding specific artists’ music
- Legal Music Sources:
- Obtain music from legal sources such as iTunes or Napster to avoid issues with strange file names
- Regular Maintenance:
- Delete duplicate songs regularly to prevent clutter
- Backup your music library consistently to avoid loss
- Technical Details in Filenames:
- Incorporate instrument type, preparation method, note, loop information, bit depth, sample rate, and number of channels for clarity
- Version Tracking and Project Templates:
- Keep track of different project versions for easy comparison and reversion
- Create project templates with common tracks, busses, and plugin settings to save time
- Documentation and Planning:
- Document all aspects of your projects, including ideas, decisions, and troubleshooting steps
- Plan the order of tracking and allocate sufficient time for each part
Implementing these strategies not only streamlines your workflow but also secures your creative outputs. By mastering file organization, you ensure that your music production process is not just efficient but also protected against potential technical hitches.
Optimizing for Speed and Accessibility
To ensure your music hard drive operates at peak efficiency, focusing on speed and accessibility is paramount. Here are actionable steps to optimize your digital workspace:
System Performance Enhancements
- Regular Restarts: Reboot your computer regularly to clear temporary files and prevent audio drop-outs, distortion, and system freezes.
- Power Management: Connect your computer to its power adapter to prevent CPU throttling and adjust your power options to avoid sleep mode and USB device suspension.
- High-Performance Settings: Activate the High Performance plan in your power options, setting both display and computer sleep times to ‘Never’ to ensure uninterrupted workflow.
- Processor and USB Settings: Adjust processor scheduling for efficiency with specific software like Serato, and disable USB Power Management to improve device recognition.
Disk and Storage Optimization
- Disk Compression: Ensure ‘Compress this drive to save disk space’ is unchecked in drive properties to enhance disk performance during recording and playback.
- Drive Partitioning: Use ‘short stroking’ to partition your hard drive, placing the OS and frequently used applications in the fastest sectors.
- External Hard Drives: Utilize an external hard drive for sample libraries and backups, opting for a fast connection like USB 3.0 or Thunderbolt for optimal performance.
Software and Driver Updates
- Operating System: Keep your OS updated for both performance and security enhancements.
- Drivers: Regularly update your graphics, network adapter, and controller drivers to ensure efficient system performance and compatibility with music production software.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll not only enhance the speed and accessibility of your music hard drive but also create a more efficient and productive digital workspace. This proactive approach to system optimization ensures that your music production process is seamless, allowing you to focus on creativity rather than technical hitches.
Creating an Effective File Structure
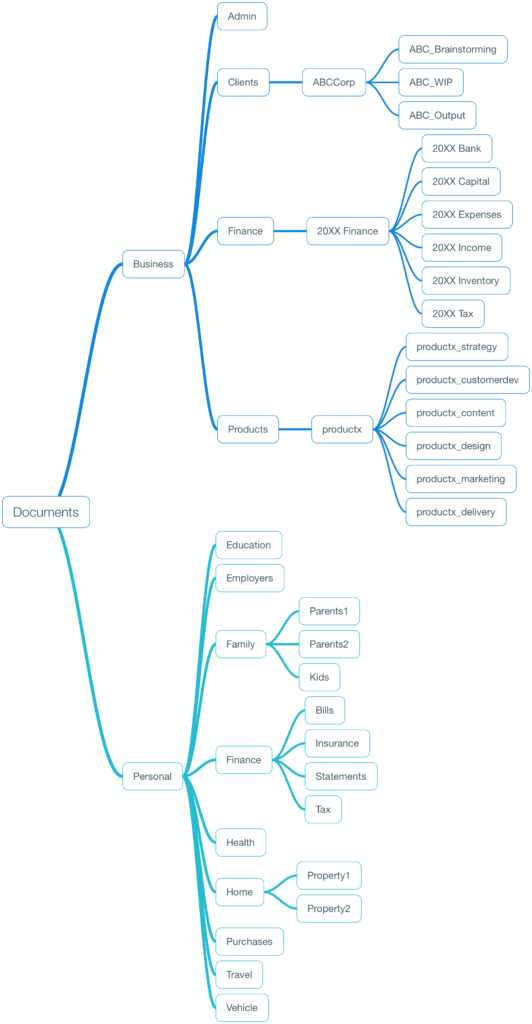
The structure only is important here, not what you might want to read inside. Creating an effective file structure on your music hard drive involves a blend of organization, foresight, and consistency. Here’s how to set up a file structure that enhances your music production workflow:
Establish a Clear Folder Hierarchy
- Project Folders: Each project should have its own dedicated folder. This helps in keeping tracks of various projects without mixing up files 1. Example: “2023-Album-Project”
- Subfolders for Elements: Inside each project folder, create subfolders for specific elements such as:
- Audio Files: Store all your recorded tracks, samples, loops, and sound effects here.
- MIDI Files: A separate folder for MIDI files ensures easy access and organization.
- Project Files: Your DAW project files go here, keeping them separate from raw audio and MIDI files.
- Samples and Plugins: Having a dedicated folder for your samples and another for plugin presets can drastically improve your workflow.
Naming Conventions and Metadata
- Descriptive Names: Use clear and descriptive names for your files and folders. Include information like the project name, date, and version number. This not only helps in identifying files at a glance but also in maintaining version control. Example: “2023-Album-Project_V1.2”
- Metadata and Tagging: Ensure your audio files are properly tagged with relevant metadata. This includes the track title, artist, album, and year of release. Double-check album information from reliable databases like FreeDB to avoid spelling mistakes and inconsistencies. Properly tagged files are crucial for efficiently indexing and organizing your music library.
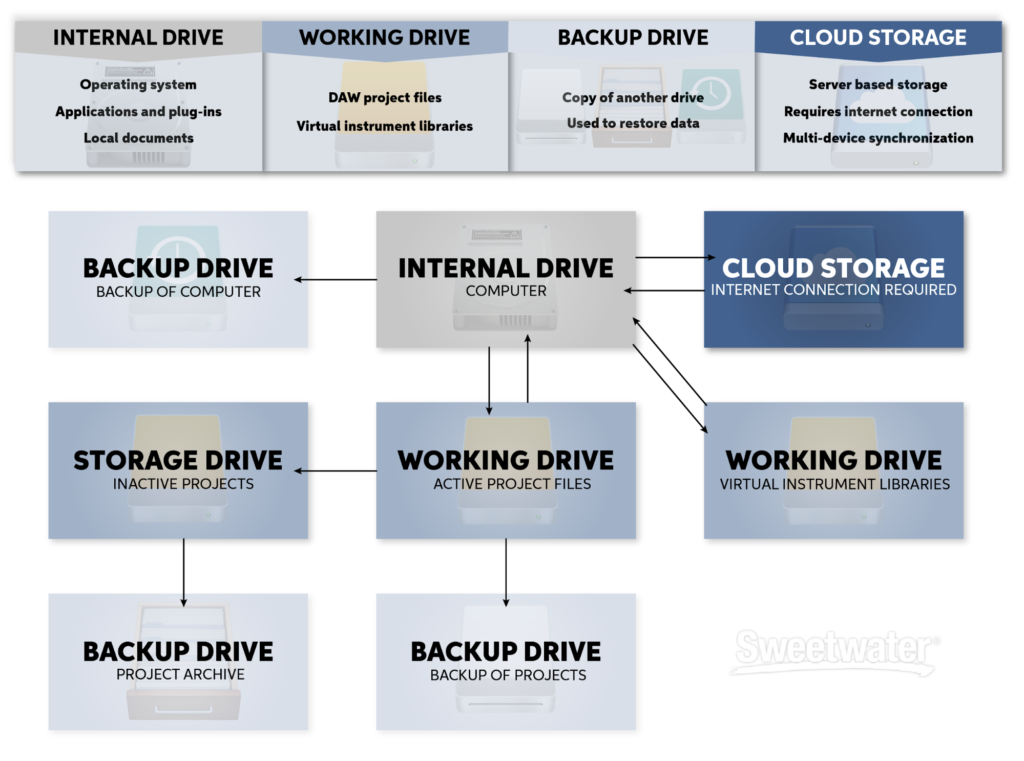
Backup and Redundancy
- Implement a Robust Backup Strategy: Regularly copy your project folder to an external drive or use cloud storage. This step is crucial in preventing data loss and ensuring that your hard work is safeguarded against technical failures.
- External Drive: Ideal for physical backups, offering quick access and portability.
- Cloud Storage: Provides an off-site backup solution, protecting your data against local disasters.
By meticulously organizing your music hard drive with a logical folder structure, adhering to a consistent naming convention, and implementing a reliable backup strategy, you set the stage for a more efficient and productive music production process. This organizational foundation not only saves time but also minimizes the frustration of searching for files, allowing you to focus on the creative aspects of music production.
Implementing a Consistent Naming Convention

Implementing a consistent naming convention for your music files and folders is a critical step in mastering file management on your music hard drive. Here’s how to do it effectively:
Develop a Standardized Naming System
- Descriptive and Understandable: Your file names should immediately convey what the file contains without needing to open it. This could include information like the artist name, track number, song title, and version if applicable.
- Sortable Format: Adding the date in the format YYYY-MM-DD at the start of the filename ensures that your files are sorted chronologically, making it easier to navigate through versions or sessions.
- Version Control: When working on different drafts, append the filename with “_V” followed by the version number. This makes it easier to track progress and revert to previous versions if needed.
Naming Convention Examples
- Single Tracks: For individual files, a format like “Artist – Track Name.mp3” is clear and concise. If the track is part of an album, consider using “Artist – Album Name – Track Number – Track Name.mp3” to maintain order within the album.
- Album Directories: When organizing albums, a directory named “Artist – Album Name” can contain files named “Track Number. Artist Name – Track Name.mp3”, ensuring each track is easily identifiable and in the correct order.
- Special Characters: Use underscores (_) instead of spaces, and hyphens (-) to separate different parts of the filename. Stick to letters, numbers, hyphens, and underscores only, avoiding special characters to ensure compatibility across different systems and software.
Community Insights
- Respect for Music Sharers: Adopting proper naming conventions is not just about personal organization; it’s also about respecting others who may interact with your files. Clear and consistent naming helps everyone involved in a project or those you share files with to easily understand and access the needed tracks.
- Avoiding Confusion: The worst scenario is removing vital information from a filename, making it difficult to identify specific versions or tracks. Always ensure your naming convention includes all necessary details.
By adhering to these guidelines, you not only streamline your own workflow but also contribute to a culture of clarity and respect within the music production community.
Leveraging Software and Tools for File Management
In the realm of music production, leveraging software and tools for file management is not just about keeping your music hard drive organized; it’s about enhancing your creative workflow and ensuring your projects are easily accessible, shareable, and secure. Here’s how you can utilize software and tools to maximize file management efficiency:
Music Tagging and Metadata Management
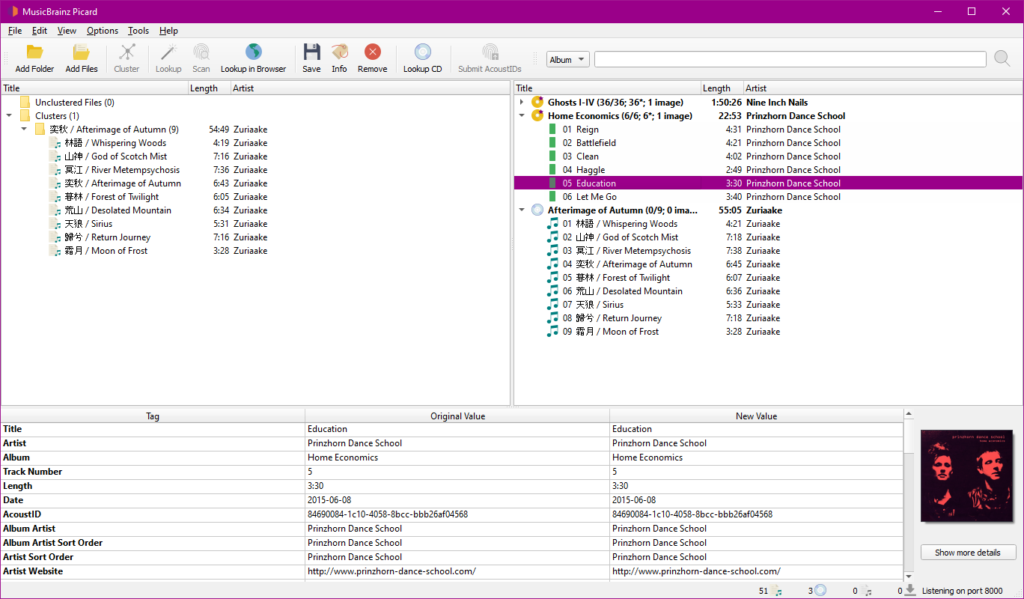
- MusicBrainz Picard: An indispensable tool for sorting files and retrieving metadata from an online database, ensuring your tracks are correctly tagged with artist, title, and album information. Modify the tagger script to tailor the date tag to display only the year, making your files easier to sort and identify.
- Mp3tag & TidyTag Music Tag Editor: Both tools are excellent for batch editing metadata, allowing you to manage a large number of files efficiently. They support a wide range of formats, making them versatile options for any music producer.
Template-Based Production & Collaborative Workflow
- DAW Templates: Create templates for different genres or project types to save time and maintain consistency across your projects. These templates can include pre-arranged instrument tracks, channel strip settings, and effects chains.
- Cloud-Based Tools: Implement project management and file sharing tools like Google Drive or Dropbox for real-time collaboration. These platforms facilitate instant feedback and streamline communication among team members, making remote music production seamless.
Optimization and Organization
- Automation and Shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with keyboard shortcuts specific to your DAW and automate repetitive tasks. This not only saves time but also reduces the cognitive load, allowing you to focus more on creativity.
- Track Colors and Labels: Assign colors and labels to tracks within your DAW. This visual organization aids in quickly differentiating between different types of tracks, instruments, or sections within your project, enhancing navigability and reducing confusion.
- Regular Maintenance: Establish a routine for reviewing and archiving or removing files that are no longer needed. Coupled with a robust backup system, this practice protects against data loss and ensures your music library remains organized and up-to-date.
By integrating these software solutions and tools into your music production workflow, you empower yourself with a streamlined, efficient, and collaborative working environment. This not only bolsters your creativity but also ensures that your projects are well-organized, secure, and easily accessible, thereby maximizing the potential of your music hard drive.
Conclusion
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the multifaceted strategies music producers can employ to master file management, extending far beyond simply optimizing a music hard drive. Effective file organization, establishing an efficient digital workspace, and implementing consistent naming conventions form the bedrock of a streamlined music production process.
These practices not only safeguard your creative outputs but also enhance your focus on creativity by minimizing the distraction of disorganized files and technical hitches. The significance of adopting tools and software for file management cannot be overstressed, as they contribute immensely to a productive, collaborative, and efficient music production workflow.
FAQs
Q: What is the best way to organize files for music production?
A: To effectively manage your music production files, start by creating main folders labeled ‘Virtual Instrument Libraries’ and ‘Audio Samples.’ Within these, make subfolders named after the specific sample library, such as ‘drum loops’ or ‘Native Instruments libraries.’ Ensure you have a separate folder for virtual instrument libraries and another for audio samples to keep everything neatly organized.
Q: How many external storage devices should a music producer have?
A: A music producer should aim to have at least three distinct hard drives. The first is the ‘operating drive,’ which houses your computer’s operating system. The second, known as the ‘music drive,’ should be dedicated to storing your project sessions and files. This setup allows for better organization and may improve system performance.
Q: What does managing audio files entail?
A: Managing audio files is a critical task for video editors, involving keeping track of and organizing audio clips to prevent clutter in the project folder. Proper audio file management is necessary to maintain an efficient workflow and ensure easy access and editing of audio files.
Q: Can you outline the structure of music production?
A: Music production can be divided into five key stages:
- Composition: This is where you create the initial musical ideas.
- Arrangement: In this stage, you arrange your musical concepts along a timeline to craft the complete piece.
- Sound Design and Production: This involves choosing and creating the sound palette for the track.
- Mixing: At this point, you adjust levels, apply effects, and blend all the elements together.
- Mastering: The final stage is mastering, where the track is polished and prepared for distribution.
This post may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you.