Are you a music producer looking to take your skills to the next level? Do you want to create your own original compositions and express your musical ideas? Look no further! In this guide, we will dive deep into the world of music composition and provide you with the tools and techniques you need to write your own music. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced producer, this comprehensive guide will help you unleash your creativity and elevate your music production game. So grab your headphones, fire up your DAW, and let’s get started!
Introduction
Music composition is an art form that allows you to create your own musical works. It is the process of conceiving and structuring musical ideas, and it offers endless possibilities for self-expression. As a music producer, writing your own music compositions can help you develop your unique sound and style, and establish yourself as a distinguished artist. Whether you’re aiming for commercial success or personal fulfillment, mastering the art of music composition is essential.
The Importance of Music Composition
Music composition plays a crucial role in the music production process. It is the foundation upon which all other aspects of music production are built. By writing your own music, you have complete control over the creative direction of your tracks. It allows you to express your emotions, tell a story, or convey a message through your music. Moreover, composing your own music sets you apart from other producers and helps you establish a unique identity in the industry.
Getting Started: How to Start a Music Composition

Starting a music composition can be an exciting yet daunting task. With so many possibilities, it’s important to set parameters and consider various factors before diving into your composition. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
Setting Parameters and Considerations
Before you begin, establish the purpose and goals of your composition. Are you writing a piece for your next recording? Is it a commemoration of an event or a tribute to someone? Determining your motivation and purpose will help guide your creative process and provide clarity to your musical ideas.
Finding Your Purpose
Knowing your purpose for writing the piece will help you in making stylistic decisions. You can focus on conveying specific emotions, telling a story, or experimenting with new techniques. Having a clear purpose will lend direction and coherence to your composition.
Utilizing Templates
Music composition templates can be valuable tools for streamlining the creative process. Lead sheets, small ensemble templates, and large ensemble templates provide a framework for organizing your musical ideas. They save time by eliminating the need to set up a score from scratch and allow you to focus on the creative aspects of composition.
Exploring Music Composition Software
Music composition software such as Sibelius and Finale can greatly enhance your workflow. These programs offer powerful tools for notation, arranging, and playback. They allow you to easily edit and refine your compositions, and provide a platform for sharing and collaborating with other musicians. Berklee Online offers courses that teach you how to use these software programs effectively.
Exploring Musical Elements
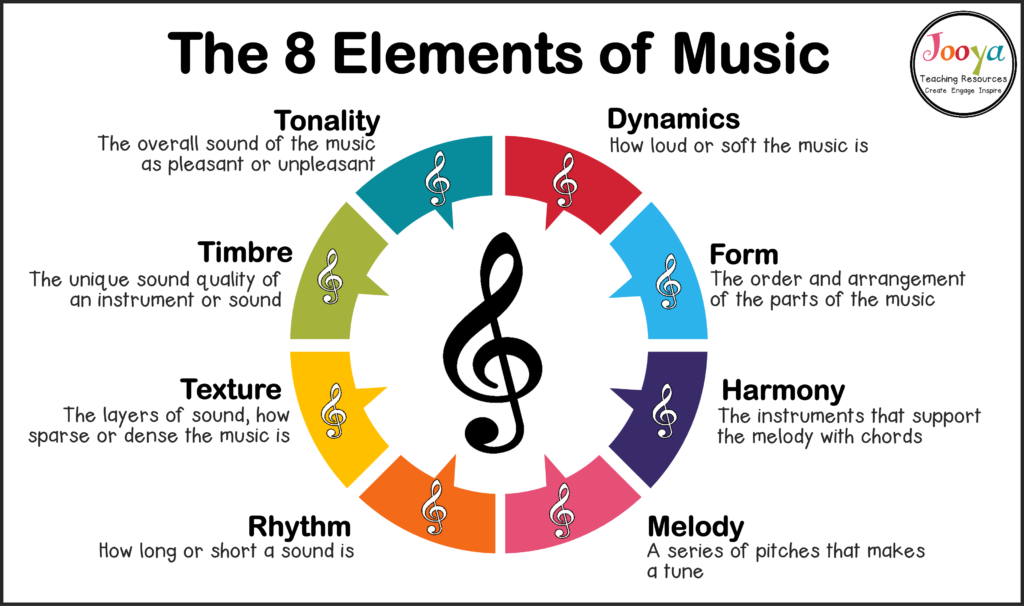
To become a skilled music composer, you must have a solid understanding of the fundamental musical elements. These elements include pitch and melody, rhythm and meter, harmony and chords, texture and timbre, and dynamics and expression. Let’s take a closer look at each of these elements:
Pitch and Melody
Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of a musical sound. Melody is the organization of pitches in a meaningful and expressive way. It is the main theme or tune that listeners can easily recognize and remember. Melodies can be simple or complex, and they provide the foundation for your composition.
Rhythm and Meter
Rhythm is the pattern of sounds and silences in music. It gives music its sense of movement and pulse. Meter refers to the organization of rhythmic patterns into regular units or measures. Understanding rhythm and meter is essential for creating grooves, building tension, and creating memorable rhythmic patterns in your compositions.
Harmony and Chords
Harmony is the combination of simultaneous sounds in music. It involves the vertical aspect of music, where multiple pitches are played or sung together to create chords. Chords provide the harmonic framework for your composition and can evoke different emotions and moods. Understanding how to create and manipulate chords is crucial for writing harmonically rich and interesting compositions.
Texture and Timbre
Texture refers to the interplay of different musical lines or voices in a composition. It can be thick or thin, dense or sparse, and it adds depth and complexity to your music. Timbre, on the other hand, refers to the quality of a sound, such as its tone color or the instrument producing it. Experimenting with different textures and timbres can help you create unique and engaging compositions.
Dynamics and Expression
Dynamics refer to the volume or intensity of a musical performance. It adds emotional depth and variety to your composition. Expression, on the other hand, involves the use of musical techniques to convey specific emotions or musical ideas. Understanding how to use dynamics and expression effectively can bring your compositions to life and create a powerful impact on your listeners.
By mastering these musical elements, you’ll have a strong foundation for creating compelling and engaging compositions.
Musical Forms and Structures
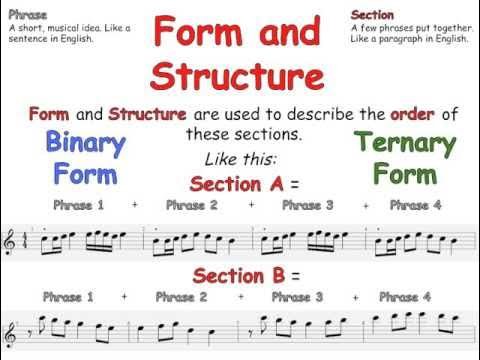
Understanding musical form is essential for organizing the various sections of your composition and creating a cohesive musical experience. Musical forms provide a blueprint for your composition and guide the listener through different sections and themes. Let’s explore some common musical forms:
Understanding Musical Form
Musical form refers to the overall structure or organization of a piece of music. It determines how different sections of the composition relate to each other and creates a sense of balance and coherence. By understanding musical form, you can create compositions that have a clear beginning, middle, and end.
Common Musical Forms
There are several common musical forms that you can explore in your compositions. These include the ternary form (ABA), the theme and variations form (A-A’-A”-A”’…), and the rondo form (ABACA or ABACABA). Each form has its own unique characteristics and provides a framework for organizing your musical ideas. Experimenting with different forms can add variety and interest to your compositions.
Choosing the Right Instrumentation
The choice of instrumentation is an important consideration in music composition. It determines the sound and timbre of your composition and can greatly impact the overall mood and character of the piece. Let’s discuss some practical and aesthetic considerations when choosing the right instrumentation:
Practical Considerations
When selecting instruments for your composition, consider the resources and expertise available to you. If you have access to a live band or orchestra, you can take advantage of a wide range of instruments and create complex and richly textured compositions. However, if you’re working with limited resources or virtual instruments, it’s important to choose instruments that will complement each other and create a balanced and cohesive sound.
Aesthetic Considerations
The choice of instruments can also be driven by aesthetic considerations. Different instruments have different tonal qualities and evoke different emotions. For example, a composition featuring a solo piano might create a sense of intimacy and introspection, while a composition with a full orchestra might evoke grandeur and drama. Consider the mood and character you want to convey in your composition and choose instruments that align with your artistic vision.
By carefully selecting the right instrumentation, you can create compositions that sound balanced, cohesive, and evoke the desired emotions in your listeners.
Selecting a Key or Tonal Center
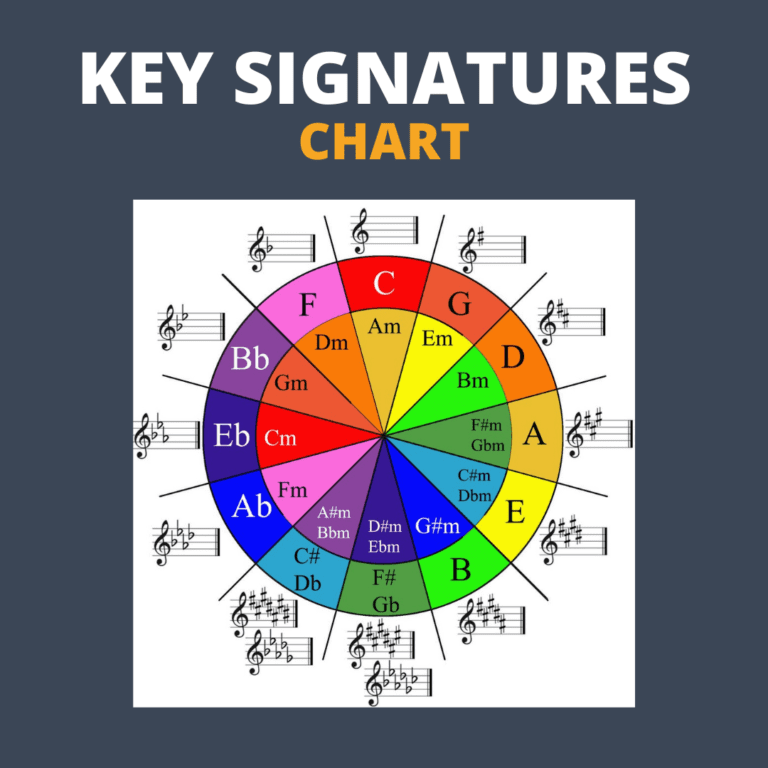
The selection of a key or tonal center is an important decision in music composition. It determines the overall tonality and harmonic framework of your composition. When choosing a key, consider the following factors:
Considering Instrumentation and Range
When selecting a key, take into account the range and capabilities of the instruments or voices you are composing for. Some instruments have limitations on certain pitches or tonalities, and choosing a key that accommodates these limitations can ensure that your composition is playable and sounds its best.
Exploring Tonalities and Modes
Experimenting with different tonalities and modes can add depth and variety to your compositions. Tonalities refer to the major or minor tonal framework of a composition, while modes offer alternative tonalities and scales that can create unique and interesting musical flavors. By exploring tonalities and modes, you can create compositions that have a distinct and captivating sound.
Determining the Length and Form of Your Piece
The length and form of your composition are important considerations that will shape the overall structure and development of your musical ideas. Determining the length and form in advance can help you create a coherent and engaging composition. Consider the following factors:
Short vs. Extended Compositions
Decide whether your composition will be a short tune, a short arrangement, or an extended composition. Shorter compositions are often used in commercial settings, such as radio airplay or background music. Extended compositions, on the other hand, allow for more complex development and exploration of musical ideas. Consider the purpose and context of your composition when determining its length.
Defining the Form
Defining the form of your composition will provide a roadmap for organizing your musical ideas. Common forms include ABA, ABAB, and ABACADA. These forms provide a structure that guides the listener through different sections and themes. By defining the form in advance, you can create a composition that has a clear and logical progression.
Exploring Harmonic Rhythm
Harmonic rhythm refers to the rate at which chords change in a composition. By varying the harmonic rhythm, you can create tension, release, and emotional impact in your music. Faster harmonic rhythm can create a sense of energy and excitement, while slower harmonic rhythm can create a more relaxed and reflective mood. Experiment with different harmonic rhythms to create the desired emotional impact in your compositions.
By determining the length and form of your composition, you can create a structure that supports your musical ideas and guides the listener through a coherent and engaging musical journey.
Enhancing Your Compositions: Techniques and Tools
To take your compositions to the next level, it’s important to explore various techniques and tools that can enhance your musical ideas. Here are some techniques you can apply to add depth and interest to your compositions:
Sequencing and Variation
Sequencing involves repeating a musical idea with some sort of variation. This can be achieved through pitch transposition, rhythmic variation, or melodic development. Sequencing adds coherence and unity to your compositions, and it can create a sense of anticipation and familiarity for the listener.
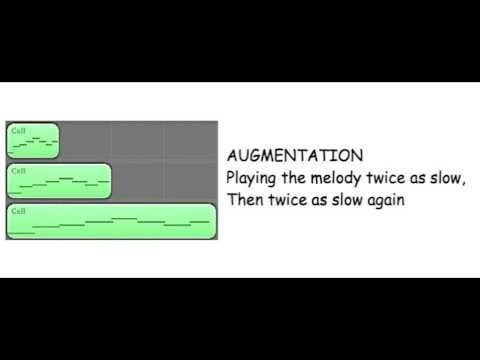
Augmentation and Diminution
Augmentation involves increasing the duration of a rhythmic element or interval, while diminution involves decreasing the duration. These techniques can be applied to create variation and build tension in your compositions. By manipulating the duration of musical elements, you can create contrast and add interest to your music.
Pitch Augmentation and Diminution
Similar to rhythmic augmentation and diminution, you can apply these techniques to widen or contract the intervals within a melodic fragment. This can create a sense of drama and variation in your compositions. Experiment with different intervallic relationships to find the right balance of tension and release in your music.
Varied Harmonic Rhythm
Harmonic rhythm refers to the rate at which chords change in your composition. By varying the harmonic rhythm, you can create tension, release, and emotional impact. Increasing the frequency of harmonic changes can create excitement and anticipation, while slowing down the harmonic rhythm can create a sense of reflection and introspection. Use varied harmonic rhythm strategically to enhance the emotional impact of your compositions.
By applying these techniques and tools to your compositions, you can add depth, interest, and variety to your musical ideas.
Music Composition Software: Sibelius and Finale

Music composition software can greatly enhance your workflow and productivity as a music producer. Two popular software programs for music composition are Sibelius and Finale. Let’s explore the benefits of using these software programs and how they can help you in your composition process:
Benefits of Music Composition Software
Music composition software offers a range of benefits. It provides a platform for notating and arranging your musical ideas, making it easier to share and collaborate with other musicians. It also allows for easy editing and refining of your compositions, giving you the flexibility to experiment and make changes as needed. Additionally, music composition software provides playback features, allowing you to hear your compositions come to life.
Introduction to Sibelius and Finale
Sibelius and Finale are two major music composition software programs widely used by composers and music producers. Sibelius offers a comprehensive set of tools for notation, arranging, and playback, while Finale provides similar features with its own unique interface and capabilities. Both programs are powerful and versatile, allowing you to create professional-looking scores and share your compositions with others.
Music Composition Books and Resources

If you want to further your knowledge of music composition, there are several books and resources available that can help you hone your skills. Here are some highly recommended music composition books:
Learning Music Composition on Your Own
Music composition books are a great way to learn the basics of music notation and composition. They provide step-by-step guidance and exercises to help you develop your composition skills. Berklee Press has published several music composition books that cover topics such as music notation, score preparation, and contemporary music notation.
Highly Recommended Music Composition Books
Some highly recommended music composition books include “Music Notation: Preparing Scores and Parts” by Jonathan Feist, “Finale: An Easy Guide to Music Notation” by Thomas E. Rudolph, and “Berklee Contemporary Music Notation” by Jonathan Feist. These books offer comprehensive guidance on music notation and composition techniques, and they are widely used by music educators and composers.
Berklee Online Music Composition Courses
In addition to books, Berklee Online offers a range of music composition courses that can help you take your skills to the next level. These courses cover topics such as contemporary composition techniques, jazz composition, film and TV composition, and music theory and composition. By enrolling in these courses, you can receive expert instruction and feedback from experienced music educators.
By exploring these resources, you can deepen your understanding of music composition and continue to improve your skills as a music producer.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between composing and arranging music? A: Composing involves creating original musical ideas and structures, while arranging involves taking existing musical material and adapting it for different instruments or ensembles.
Q: Can I compose music without knowing how to read sheet music? A: While reading sheet music can be beneficial, it is not a requirement for composing music. Many successful composers have created music through aural and experimental methods.
Q: How can I find inspiration for my compositions? A: Inspiration can come from various sources, such as personal experiences, emotions, nature, other music, or visual arts. Keeping an open mind and actively seeking inspiration can help fuel your creativity.
Q: Can I compose music using digital audio workstations (DAWs)? A: Yes, DAWs provide a range of tools and virtual instruments that can facilitate composition. They allow you to create, arrange, and manipulate musical ideas digitally.
Q: Should I focus on one genre of music or explore different genres in my compositions? A: Both approaches can be beneficial. Focusing on one genre allows you to develop a deep understanding of its conventions and techniques. However, exploring different genres can broaden your musical horizons and provide new creative possibilities.
Q: How can I receive feedback on my compositions? A: Sharing your compositions with peers, mentors, or online communities can provide valuable feedback and constructive criticism. It can help you refine your compositions and gain new perspectives on your music.
Q: What are some common challenges in music composition, and how can I overcome them? A: Common challenges in music composition include writer’s block, self-doubt, and lack of inspiration. Overcoming these challenges requires persistence, experimentation, and seeking inspiration from various sources.
This post may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you.








